Which Organelles Are Found Only In Animals?
Animal Cell Structure
Animal cells are typical of the eukaryotic jail cell, enclosed by a plasma membrane and containing a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. Unlike the eukaryotic cells of plants and fungi, animal cells do not have a cell wall. This feature was lost in the distant past by the single-celled organisms that gave ascent to the kingdom Animalia. Most cells, both beast and institute, range in size between one and 100 micrometers and are thus visible only with the assistance of a microscope.
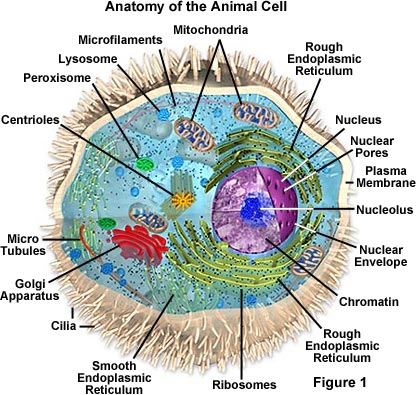
The lack of a rigid cell wall allowed animals to develop a greater multifariousness of prison cell types, tissues, and organs. Specialized cells that formed nerves and muscles�tissues impossible for plants to evolve�gave these organisms mobility. The ability to movement almost past the use of specialized muscle tissues is a hallmark of the animal world, though a few animals, primarily sponges, do not possess differentiated tissues. Notably, protozoans locomote, but it is only via nonmuscular means, in effect, using cilia, flagella, and pseudopodia.
The animal kingdom is unique among eukaryotic organisms because most creature tissues are leap together in an extracellular matrix by a triple helix of protein known as collagen. Establish and fungal cells are jump together in tissues or aggregations past other molecules, such equally pectin. The fact that no other organisms utilize collagen in this manner is one of the indications that all animals arose from a mutual unicellular antecedent. Bones, shells, spicules, and other hardened structures are formed when the collagen-containing extracellular matrix between animal cells becomes calcified.
Animals are a large and incredibly diverse group of organisms. Making up about iii-quarters of the species on World, they run the gamut from corals and jellyfish to ants, whales, elephants, and, of form, humans. Beingness mobile has given animals, which are capable of sensing and responding to their surround, the flexibility to prefer many different modes of feeding, defense, and reproduction. Unlike plants, however, animals are unable to manufacture their own food, and therefore, are always directly or indirectly dependent on constitute life.
Almost creature cells are diploid, meaning that their chromosomes be in homologous pairs. Different chromosomal ploidies are likewise, yet, known to occasionally occur. The proliferation of beast cells occurs in a variety of ways. In instances of sexual reproduction, the cellular process of meiosis is first necessary so that haploid daughter cells, or gametes, can be produced. 2 haploid cells then fuse to form a diploid zygote, which develops into a new organism equally its cells divide and multiply.
The primeval fossil evidence of animals dates from the Vendian Menstruation (650 to 544 meg years ago), with coelenterate-type creatures that left traces of their soft bodies in shallow-water sediments. The kickoff mass extinction ended that menstruum, merely during the Cambrian Flow which followed, an explosion of new forms began the evolutionary radiation that produced nearly of the major groups, or phyla, known today. Vertebrates (animals with backbones) are non known to accept occurred until the early Ordovician Catamenia (505 to 438 one thousand thousand years ago).
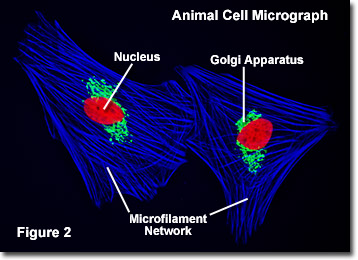
Cells were discovered in 1665 by British scientist Robert Hooke who first observed them in his crude (past today'southward standards) seventeenth century optical microscope. In fact, Hooke coined the term "cell", in a biological context, when he described the microscopic structure of cork like a tiny, bare room or monk's jail cell. Illustrated in Figure 2 are a pair of fibroblast deer skin cells that accept been labeled with fluorescent probes and photographed in the microscope to reveal their internal structure. The nuclei are stained with a red probe, while the Golgi apparatus and microfilament actin network are stained green and bluish, respectively. The microscope has been a fundamental tool in the field of cell biology and is frequently used to observe living cells in culture. Use the links below to obtain more than detailed information well-nigh the various components that are found in animal cells.
-
Centrioles - Centrioles are self-replicating organelles made up of nine bundles of microtubules and are plant only in animal cells. They appear to help in organizing jail cell division, just aren't essential to the process.
-
Cilia and Flagella - For single-celled eukaryotes, cilia and flagella are essential for the locomotion of private organisms. In multicellular organisms, cilia office to move fluid or materials past an immobile cell also as moving a cell or grouping of cells.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum - The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of sacs that manufactures, processes, and transports chemical compounds for use within and outside of the cell. It is connected to the double-layered nuclear envelope, providing a pipeline between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
-
Endosomes and Endocytosis - Endosomes are membrane-spring vesicles, formed via a circuitous family of processes collectively known equally endocytosis, and found in the cytoplasm of virtually every animal cell. The bones mechanism of endocytosis is the opposite of what occurs during exocytosis or cellular secretion. It involves the invagination (folding inwards) of a prison cell's plasma membrane to surroundings macromolecules or other thing diffusing through the extracellular fluid.
-
Golgi Apparatus - The Golgi apparatus is the distribution and shipping department for the prison cell's chemical products. It modifies proteins and fats congenital in the endoplasmic reticulum and prepares them for export to the exterior of the jail cell.
-
Intermediate Filaments - Intermediate filaments are a very broad class of fibrous proteins that play an important role as both structural and functional elements of the cytoskeleton. Ranging in size from 8 to 12 nanometers, intermediate filaments office equally tension-bearing elements to help maintain cell shape and rigidity.
-
Lysosomes - The main part of these microbodies is digestion. Lysosomes break downwards cellular waste products and debris from exterior the prison cell into uncomplicated compounds, which are transferred to the cytoplasm as new cell-edifice materials.
-
Microfilaments - Microfilaments are solid rods fabricated of globular proteins called actin. These filaments are primarily structural in function and are an of import component of the cytoskeleton.
-
Microtubules - These straight, hollow cylinders are found throughout the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells (prokaryotes don't accept them) and carry out a diversity of functions, ranging from transport to structural support.
-
Mitochondria - Mitochondria are ellipsoidal shaped organelles that are found in the cytoplasm of every eukaryotic cell. In the animal prison cell, they are the main power generators, converting oxygen and nutrients into energy.
-
Nucleus - The nucleus is a highly specialized organelle that serves every bit the information processing and administrative center of the cell. This organelle has two major functions: it stores the jail cell's hereditary material, or DNA, and it coordinates the cell's activities, which include growth, intermediary metabolism, protein synthesis, and reproduction (cell division).
-
Peroxisomes - Microbodies are a various group of organelles that are found in the cytoplasm, roughly spherical and spring by a unmarried membrane. There are several types of microbodies but peroxisomes are the most common.
-
Plasma Membrane - All living cells have a plasma membrane that encloses their contents. In prokaryotes, the membrane is the inner layer of protection surrounded by a rigid cell wall. Eukaryotic animate being cells have just the membrane to comprise and protect their contents. These membranes as well regulate the passage of molecules in and out of the cells.
-
Ribosomes - All living cells contain ribosomes, tiny organelles equanimous of approximately lx percent RNA and forty per centum protein. In eukaryotes, ribosomes are made of four strands of RNA. In prokaryotes, they consist of three strands of RNA.
In addition the optical and electron microscope, scientists are able to use a number of other techniques to probe the mysteries of the animal jail cell. Cells tin can be disassembled past chemic methods and their individual organelles and macromolecules isolated for study. The process of cell fractionation enables the scientist to prepare specific components, the mitochondria for case, in large quantities for investigations of their composition and functions. Using this approach, prison cell biologists have been able to assign various functions to specific locations inside the cell. However, the era of fluorescent proteins has brought microscopy to the forefront of biology by enabling scientists to target living cells with highly localized probes for studies that don't interfere with the delicate balance of life processes.
Back TO Jail cell STRUCTURE HOME
Dorsum TO FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY OF CELLS
Questions or comments? Send us an email.
© 1995-2022 by Michael Westward. Davidson and The Florida State University. All Rights Reserved. No images, graphics, software, scripts, or applets may be reproduced or used in any manner without permission from the copyright holders. Employ of this website means you agree to all of the Legal Terms and Weather set forth by the owners.
This website is maintained by our
Graphics & Web Programming Team
in collaboration with Optical Microscopy at the
National Loftier Magnetic Field Laboratory.
Last modification: Friday, Nov 13, 2015 at 02:18 PM
Access Count Since October 1, 2000: 6354446
Microscopes provided by:
Source: https://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/animalcell.html
Posted by: wisehumpertle.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Which Organelles Are Found Only In Animals?"
Post a Comment